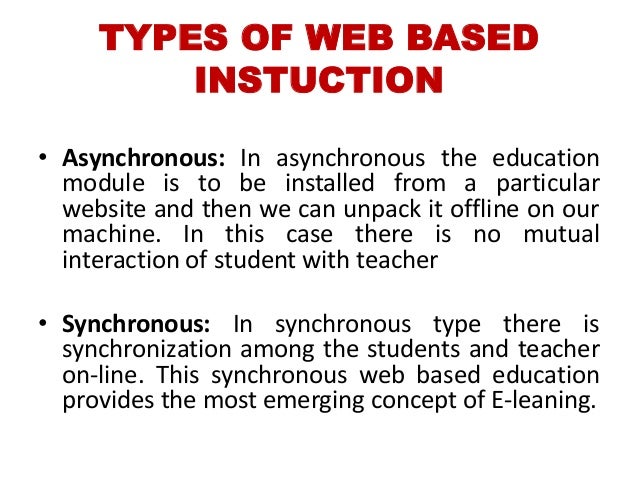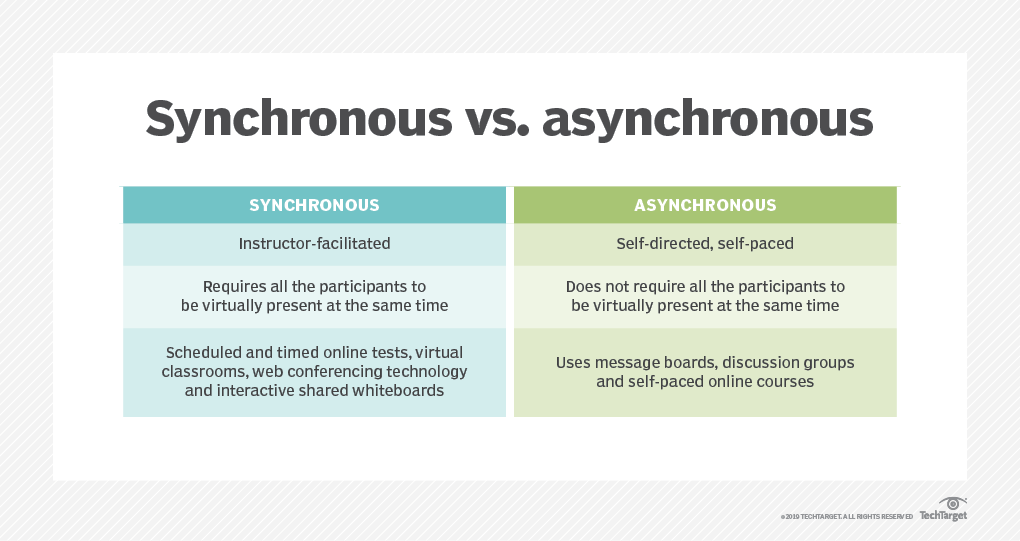
INSTRUCTIONAL SOFTWARE
Defined as computer programs designed to deliver instruction or to assist in the delivery of instruction on a specific topic. This type of software’s sole purpose is to support instruction and/of learning.
Instructional software is one of many resources teachers can use to implement educational technology into the classroom. Educational / Instructional software can be found in many formats: purchase hard copies, downloaded or used virtually. The purpose of having software in the classroom is to help students learn content and/or skills on a variety of topics. The term Relative Advantage was coined by Everett Rogers and refers to "the benefits of a new method (or resources) has over the old one " (Roblyer, 2006, p.53). There relative advantages for using software as instructional delivery is that it could be used as a supplemental resource for helping students master content.
TYPES OF INSTRUCTIONAL SOFTWARE
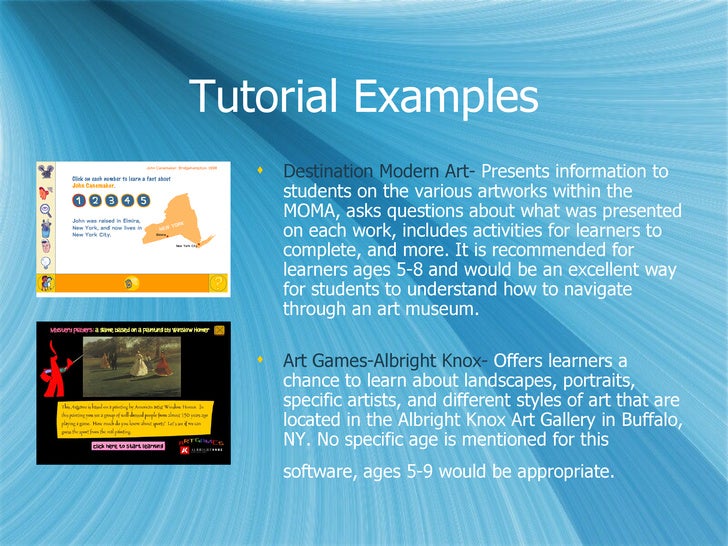
1. TUTORIAL SOFTWARE

- Act like a human tutor by providing the all information and instructional activities a learner needs to master a topic, information, summaries, explanation, practice routine, feedback and assessment.
- Students access an entire instructional program on a particular topic. It is a stand-alone unit and does not supplement other instruction.
- Tutorial Software is an instructional sequence on a topic that is similar to what the teacher instruction is in the classroom. Tutorials are mean to be used as a self-contained supplemental instructional resource.
- Linear tutorials give the same instruction sequence of explanation, practice and feedback to all learners
- Branching Tutorial: provides more sophisticated instructions that direct learners on their own personal path depending on how they respond to the question right or wrong.
- The benefits include user control, appropriate pedagogy, and adequate feedback adjusting to user responses and have record keeping. Relative advantage: Interactive, entertaining, self-guided, self-paced.
- This method is most a teachers classroom instruction. It is usually used as the unit of teaching and not as a supplement. Gagne said that good tutorial software should address all nine instructional events. There are 2 categories when talking about tutorials. The first is Linear, its simple and gives the same instruction and feedback to everybody in the class. Branching is a little more complex. It directs students on different paths based on the answers that students gives.
- The tutorials should not replace the teachings form the teacher. It can be used as a review of the instruction, another learning strategies and can be used when the teacher is not available.
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1T-rsltsWnM
Video Tutorials Khan Academy provides thousands of free video tutorials that walk students through different content. Video tutorials have their upside and downside. The upside for video tutorials is that they can be paused and rewound at any time to allow the student to review content or even write down information or draw diagrams provided in the tutorial. The downside for video tutorials is that many of them do not provide any text based information unless it is provided in the video via a text slide or if the video shows a lecture.
Linear Tutorial
With linear tutorials, the software will provide the student with the same instructional sequence of information, an animation, a conclusion, review or quiz, and then some feedback. Since they are self-paced, they allow the student to review material if needed without slowing down the rest of the class.
2. SIMULATION SOFTWARE

Models real or imaginary systems to show how those systems or similar ones work or demonstrate underlying concept.
Educational software tools that simulate the live learning experience of the students.
Simulation software is either a computerized model of a real or imagined system that is designed to teach how a system works. When students use a simulation they must choose tasks and the order in which to complete them. There are two types of simulation:
1. Those that teach about something:
· Physical simulations allow users to manipulate things or a process on the screen;
· Iterative simulations where processes can be sped up or slowed down so the user can watch the events unfold.
2. Those that teach how to do something.
· Procedural simulation which teach a sequence of steps to perform certain procedures;
· Situational simulations provide users with hypothetical problems or situations that they can react to.
- Simulations can be used in place of or a supplement to lab experiments, role playing or even a field trip. They can be used to introduce or clarify a topic, foster exploration and process learning and can be used as individual or group work. Robyler explains that a good software simulation will provide a "clear set of direction" and most important "students [will be able] to use it rapidly and easily" (2010, p.91). Relative advantage: Interactive, self-guided, self-paced, entertaining, reduces teacher preparation time.
- This is best described as a computerized model of a real or imagined system that is designed to teach how the system works. Most simulations make the student choose tasks to do or the order in which to do them. There are 2 mail types of simulations, Ones that teach about something and one that’s teaches how to do something.
- Simulations that teach about something are usually physical or iterative. Simulations that teach how to do something are usually procedural or situational. The best benefit has been in the field of science. But that doesn’t mean that the other subject are left out. There are many benefits to using simulations. A few examples are that they compress time, it gets the students involoved, it makes experiments safe, makes the impossible become possible, it saves money and resources, and it allows for students to understand complex processes.
http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/gravity-and-orbits

3. DRILL AND PRACTICE

- Allows learners to work problems or answer questions and get feedbacks and correctness.
Provides opportunities for students to work on problems or examples one at a time and then receive feedback on their performance.
- Drill and Practice software allows students to work example items one at a time. This type of software will typically provide feedback to the student. However, the type of feedback does vary from program to program. Types include:ls: these are more sophisticated and the next question is determined by whether the question at hand was answered correctly or not;
Extensive feedback: students will receive feedback as to why the answer was wrong, though this is sometimes mistaken for a tutorial as the feedback can be very detailed.
Potential use for Drill and Kill is to supplement or to replace worksheets and homework exercises and/or prepare students for an upcoming test. Guidelines: There needs to be a limit set of somewhere between 10 to 15 minutes per day. Drill and Kill can be set-up as a working station for individual use. Relative advantage: Interactive, self-guided, self-paced, entertaining.
Math Board, and iPad app for education by Pala Software. There is a five dollar cost per iPad. However the drill and kill practice software is intense and will be perfect for practice mathematics. The software is designed with students in mind that are working on math a problem that emulates working on a chalkboard. The software is also designed to build up math skills and strengthen a child's self-esteem by being able to work out problems. The advantages of this software include:
Excellent interface
Scratch area to allow child to solve problem by writing
Deep options for configuring the app
Math tables and problem solvers
Ability to email results of quiz
Results are stored in the application
- This method allows learners to work problems or answer questions and get feed back on correctness. The feedback is usually as simple as “OK” or “No Try Again”. There are many benefits to this software. A few are that it gives immediate feedback, its motivating because the kids enjoy being on the computer, and it saves the teacher time. Teachers can use this software for the replacement of worksheets or even as homework. The best way might even be to help the student prepare for test.
http://oswego.org/ocsd-web/games/mathmagician/cathymath.html

4. EDUCATIONAL GAMES

- Technology based games link the world of gaming, entertainment and education, i.e. edutainment, together in ways that encourage both fun and learning. Instructional games provide the means for learning activities that have rules and can provide a sense of competition. The whole purpose is to keep students motivated and engaged while actually working on a curriculum topic. They can be used in place of worksheets and exercises, to be used in group work, and/or as a reward / competition. As Robyler stated, "Instructional games add game-like rules and/or competition to learning activities" (2010, p.84). Though be sure not to overuse this type of software and they should be aligned to curriculum lessons and state standards. Relative advantage: Interactive, entertaining, reduces teacher preparation time.
- Most students like these the most. They have appealing formats and activities and good instructional value. Plus the students feel like they are planning games but they are actually learning. This should not be an everyday occurrence but it is good for a reward. The main benefit form these games are that it makes the classroom fun and the students want to learn. The main way these games are incorporated into the classroom is in place of worksheets, to help teach cooperative group working skills and the big on is s an award.
http://www.starfall.com